(Downloads - 0)
For more info about our services contact : help@bestpfe.com
Table of contents
Introduction
1 – General Introduction
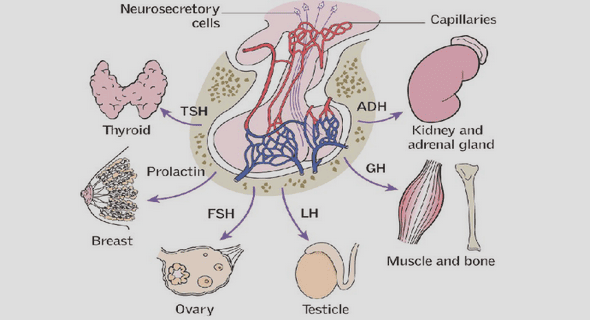
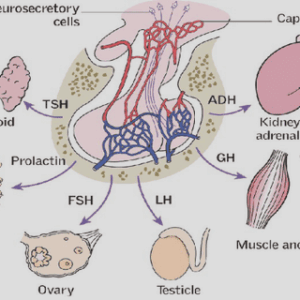
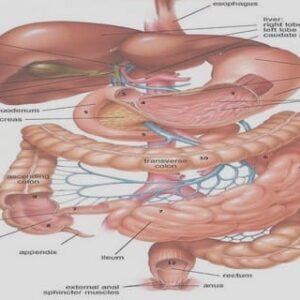
2 – Development of the enteric nervous system
I – Overview of the development of the ENS
II – Regulation of the neuron numbers in the ENS
A – Embryonic proliferation and death
B – Post Natal proliferation and death
1 – Evolution of the number of enteric neurons after birth
2 – Evidence for ongoing neurogenesis
3 – Neuronal Diversity in the ENS
I – Introduction
III – Types of enteric neurons defined by classical studies
A – Myenteric plexus
2 – Sensory (afferent) neurons
3 – Interneurons.
4 – Intestinofugal neurons
B – Submucosal plexus
1 – Secretomor/Vasodilator neurons
2 – IPANs
3 – Other types
C – Conclusion on the detection of enteric neurons types.
D – Glia.
IV – Types of enteric neurons newly defined by single cell transcriptomics.
V – Differentiation of enteric neurons into their different types.
A – Timing of neuronal diversification.
B – Mechanisms of neuronal differentiation
VI – Transcriptional control of the ENS development
4 – The transcription factor TBX3
I – The T-Box family of TFs.
II – Tbx3 in stem cells
III – Tbx3 in cancer
IV – Developmental roles of Tbx3
V – Tbx3 and the enteric nervous system
5 – Hmx2 and Hmx3 in development
I – Hmx2 and Hmx3 during embryonic development
II – Expression of Hmx2/3 in the nervous system
Results
1 – Article 1
2 – Article 23 – Unpublished results
I – Genetic interaction between ErbB3 and Ret
II – Hmx2 and Hmx3 knockouts
A – Construction
B – Phenotype of the Hmx knockouts
III – Role of Tbx3 in the development of the ENS
A – Expression of Tbx3 in the ENS
B – Gross phenotype of a Tbx3 conditional KO
C – Histological analysis of the ENS of Phox2b::Cre; Tbx3lox/lox mutants
Material and Methods
References