Get Complete Project Material File(s) Now! »
Web Service Level Agreement
In addition to a regular SLA, there are additional SLAs that deal with different kinds of services. One of these services are Web Service Level Agreement (WSLA) and to a certain point it is very similar to a regular SLA, but since we add technology to the picture, and most often, a third party management/monitoring provider more information has to be included in the WSLA. The WSLA Language Specification (Dan, Frank, Ludwig, Keller, King, V1.0, 2003) not only include the SLA components mentioned in our SLA part, but also include:
-level and business
process level service parameters such as response time and throughput, and measures to be taken in case of deviation and failure to meet the asserted service guarantees, for example, a notification of the service customer.?? What IBM indicate, and what others agree to (Patel, Ranabahu & Sheth 2009) is that WSLA needs to focus even more on metrics to measure if the service bought and received measure up to the levels agreed upon. This puts focus onto Quality of Service (QoS) and how this is measured. According to Patel et al. (2009) an example of WSLA measures is transactions per hour. By providing that kind of information, a company can make a statistical analysis to determine the QoS and if the SLA has been breached.
Cloud Service Level Agreement
If we take the two previous SLAs we have mentioned into consideration and compare it to the dynamic and scalable nature of Cloud Computing, significant changes need to be made to the SLA to be aligned with the Cloud environment. While WSLA is closer to the solution than a standardized SLA, the measurements have to be different. Because the environment is dynamic, the measures have to be dynamic as well. Patel et al (2009) propose that the parties add these measures to the picture;; usage and cost. When the Cloud services are in use, these measures have to be adapted according to usage, i.e. when the services increases in scale, the measures have to be adapted to that. This is the thinking one has to apply to make a more appropriate SLA for the Cloud Computing environment.
Risk definition
The top risks we are discussing in this thesis are from the European Network and Information Security Agency (ENISA 2009), Computer Security Alliance (CSA 2010) and National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and they are:
? Loss of Governance: The Client ceding control to a Cloud Provider on multiple issues
? Lock In: The difficulty of a customer moving from one Cloud provider to another.
? Isolations Failure: The failure of hardware separating storage, memory, routing and even reputation between different tenants.
? Compliance Risk: Investment in achieving certification may be put at risk by moving to the Cloud.
? Management Interface Compromise: Customers management interfaces of a Public Cloud provider are accessible through the Internet and mediate access to larger sets of resources, which pose an increased risk.
? Data Protection: The ability of the customer to check the data handling practices of the Cloud provider and to ensure that the data is treated in a lawful manner.
? Insecure or incomplete data deletion: Customer requesting that their data is deleted and it is not completely removed or deleted due to duplication.
? Malicious Insider: Damage caused by a person that has access to the Cloud. CSA 2010
? Abuse and Nefarious Use of Cloud Computing: Easy access and lack of control of who is using Cloud Computing can provide entrance for malicious people
? Insecure Interfaces and APIs: Authentication and reusable aces tokens/passwords have to be properly managed or security issues will rise.
? Malicious Insider: Lack of insight at the Cloud ?????????? employees can trigger risks if employees have malicious intent and access to information he/she should not have.
? Shared Technology Issues: With scalability come shared technology issues since the provider is using their own resources to provide more for the clients during peaks. With sharing technology the risk of hypervisors appear since hypervisors work in between different clients.
? Data Loss and Leakage: Improper deletion or backup of data records can lead to unwanted duplication of data that becomes available when it should not exist
? Account or Service Hijacking: Phishing for credentials to get access to sensitive data
? Unknown Risk Profile: No insight in what the provider do to keep your data safe or doing updates, patches etc.
1 Introduction
1.1 Background
1.2 Problem .
1.3 Purpose
1.4 Perspective .
1.5 Delimitation
1.6 Definitions
2 Methodology
2.1 Research philosophy
3 Theoretical Framework .
3.1 Cloud Computing .
3.2 Cloud Computing Overview model
3.3 Cloud Computing Characteristics
3.4 SPI Overview Model
3.5 Software as a Service
3.6 Platform as a Service
3.7 Infrastructure as a Service
3.8 Cloud Deployment Models
3.9 Cloud Computing Vendors Model
3.10 Multi-tenancy
3.11 Service Level Agreement
3.12 Risk definition
3.13 Security
3.14 Trust
4 Research Questions
5 Method
6 Empirical Findings.
7 Analysis
8 Conclusion
9 Discussion
10 References
GET THE COMPLETE PROJECT
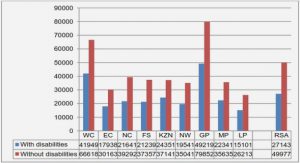
Cloud Computing -Security Risks, SLA and Trust-