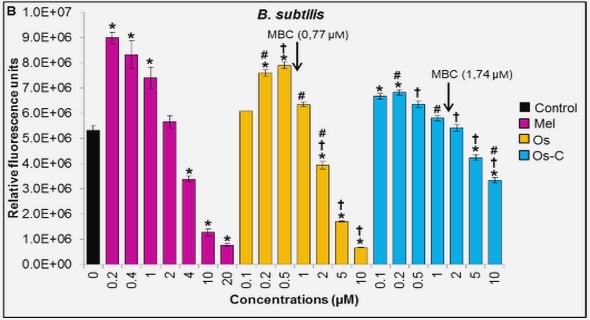
(Downloads - 0)
For more info about our services contact : help@bestpfe.com
Table of contents
Introduction
Chapter I –Nuclear Receptors: general concepts
1.1 Basic structure and molecular functions of nuclear receptors
1.2 Mechanisms of activation
1.3 NRs coregulators
1.4 NRs and disease
2.1 Structural and expression pattern
2.3 Agonists/Antagonists
2.4 Action mechanism
2.4.1 PGC-1 coactivators
2.4.2 Repressors
2.5 Post-translational modifications
2.6 Physiological functions
Chapter III–Epigenetics
3.1 The role of Epigenetics
3.2 Histone modification
3.3 Histone modification mechanism in transcription
3.4 Histone methylation
3.5 Methylation and disease
Chapter IV–Histone lysine demethylation
4.1 Histone lysine specific demethylase 1 ( LSD1)
4.2 LSD1 represses gene expression
4.2.1 With BHC and CoREST
4.2.2 With NuRD
4.3 LSD1 activates gene expression
4.4 LSD1 demethylates more than histone
4.5 Biological effects of LSD1
4.6 LSD1 and metabolism
Chapter V–Nuclear Respiratory Factor 1 (NRF1)
5.1 General introduction
5.2 NRF1 and disease
Chapter VI–Histone methyltransferases (HTMs)
6.1 Identification of SET7 and its structural analysis
6.2 SET7 mediates H3K4 mono-methylation
6.3 Physiological role of H3K4 methylation
6.4 Non-histone lysine methylation
6.5 Examples of SET7 mediated non-histone methylation and biological effects
6.5.1 SET7-mediated lysine methylation and protein stability
6.5.2 SET7-mediated lysine methylation and transcriptional activity
6.5.3 SET7-mediated lysine methylation and cellular location
6.6 SET7 involvement in disease
Chapter VII— ETS family
7.1 General introduction of ETS family and structure
7.2 Biological roles
7.3 ETS1
7.3.1 Structure of human ETS1
7.3.2 Transcriptional regulation
7.3.3 Physiological role of ETS1
7.4 Conclusion
Results
General introduction of article 1
General introduction of article 2
General Introduction of project 3
Discussion and perspective
Common aspects between both two complexes.
General conclusion
RNA-seq information and Oligonucleotides
Table 1. SET7-modulated genes
Table 2. Genes modulated by siSET7 and siERR
Table 3. Genes modulated by siSET7, but not by siERR.
Table 4. Genes modulated by siERR, but not by siSET7.
Table 5. Oligonucleotides used in this study
References
ANNEXE 1
Publication list
ANNEXE 2
Articles published as first author