(Downloads - 0)
For more info about our services contact : help@bestpfe.com
Table of contents
General Introduction
Chapter 1: Context and State of the art of Indoor Positioning
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Indoor positioning: a critical need
1.2.1 Context
1.2.2 General definitions
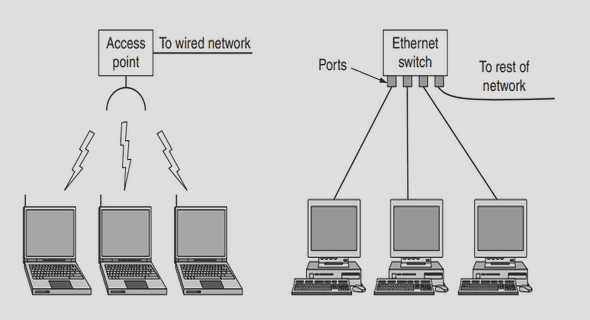
1.3 Indoor Positioning Systems
1.3.1 Infrared (IR) Positioning Systems
1.3.2 Ultra-sound Positioning Systems
1.3.3 Radio Frequency (RF) Positioning Systems
1.3.4 Alternative systems
1.4 Measuring Principles
1.4.1 RF Metrics for Wireless Localization
1.4.2 Scene Analysis
1.4.3 Proximity
1.4.4 Conclusion
1.5 Objectives
1.6 Conclusion
Bibliography
Chapter 2: Multi carrier communication signals
2.1 Introduction
2.2 General principle of MC based TDOA estimation
2.3 Multi carrier based positioning systems and OFDM solutions
2.3.1 Blind solution
2.3.2 Training solution
2.3.3 Alternative solution
2.3.4 OFDM based positioning
2.3.5 Conclusion
2.4 Data modulation
2.4.1 QPSK Based Communication System
2.4.2 SNR calculation
2.4.3 Simulation results
2.5 OFDM communication system
2.5.1 Transmitter/Receiver module
2.5.2 Guard Interval
2.5.3 Guard Band and roll of factor
2.6 MATLAB implementation
2.6.1 Transmission part
2.6.2 Reception part
2.7 Channel Estimation
2.7.1 Pilot block
2.7.2 Mathematical derivation
2.7.3 Channel estimation testing
2.8 Conclusion
Bibliography
Chapter 3: OFDM based TDOA estimation
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Algorithms for TDOA-based positioning
3.3 Definition of the direct model
3.3.1 Frequency limitation
3.3.2 Signal model
3.3.3 Energy based approach
3.3.4 Channel based approach
3.4 Inverse problem: TDOA extraction
3.4.1 Large TDOA
3.4.2 Small TDOA
3.4.3 Very small TDOA
3.4.4 Cramer Rao Bound Limit
3.5 Communication parameters effect
3.5.1 Estimation of the coefficients ,
3.5.2 Number of pilots
3.6 Communication environment effect
3.6.1 Multipath modeling
3.6.2 Emulating Multipath
3.6.3 Multipath effect reduction
3.7 Conclusion
Bibliography
Chapter 4: Experimental setup and results
4.1 Presentation of the environment
4.1.1 The controlled electromagnetic room
4.1.2 Radiating devices
4.1.1 Amplifier
4.1.2 Arbitrary waveform generator
4.1.3 Digital storage oscilloscope
4.1.4 Conclusion
4.2 SISO communication system setup
4.2.1 The transmitter
4.2.2 The receiver
4.2.3 Signal acquisition and I-Q constellation
4.2.4 OFDM communication performances
4.2.5 Channel estimation
4.3 Direct and Inverse models validation
4.3.1 MISO configuration
4.3.2 Baseline calculation
4.3.1 Calibration MISO system
4.3.2 MISO configuration for TDOA estimation
4.3.3 Direct model validation
4.3.4 Inverse model validation
4.3.5 Multipath effects
4.4 Conclusion
Conclusions and perspectives