(Downloads - 0)
For more info about our services contact : help@bestpfe.com
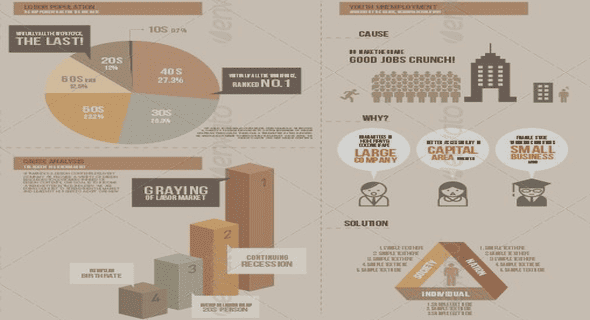
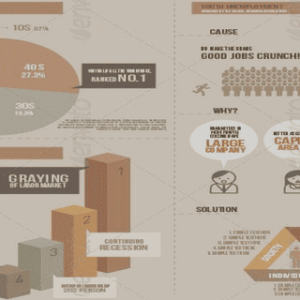
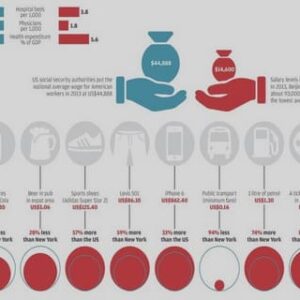
Table of contents
I Economic integration, trade policies, and institutional reforms
1 Border Effects and East-West Integration
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Border Effects and Trade Potential
1.3 Theoretical Discussions
1.3.1 A differentiated-good trade structure
1.3.2 The fixed-effects specification
1.3.3 The odds specification
1.3.4 The friction specification
1.3.5 Differences in consumer preferences
1.4 Estimating Border Effects Across Europe
1.4.1 Estimated trade equations
1.4.2 Estimations for the manufactured sector
1.4.3 Estimations with industry level data
1.5 Trade Potential and East-West European Integration
1.6 National Product Differentiation vs. Monopolistic Competition
1.7 Conclusions
2 Trade Liberalization and Institutional Reforms
2.1 Introduction
2.2 European Trade Liberalization and Institutional Changes
2.3 The Trade Model
2.4 The Data
2.5 Baseline Estimations and Results
2.6 Endogeneity Issues
2.7 Trade Policy vs. Institutional Reforms
2.8 Distinguishing among Institutions
2.9 Conclusion
II The role of social and business networks in international trade patterns
3 Trade in Cultural Goods and Social Networks
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Cultural Goods and Social Networks
3.3 The Gravity Model and Data
3.4 International Trade and Social and Cultural Ties
3.5 A Measure of the Intensity of Social Networks
3.6 Information and Preference Effects
3.7 Conclusions
4 Migrant Associations, Trade, and FDI
4.1 Introduction
4.2 Networks, Immigrants, and Migrant Associations
4.3 The Model
4.3.1 A Trade Model with Social and Business Networks
4.3.2 A Model of FDI with Network Effects
4.4 The Data and Stylized Facts on Migrant Associations
4.5 Foreign Trade in the Presence of Ethnic Networks
4.6 French Subsidiaries and Cross-border Networks
4.7 Conclusion