Get Complete Project Material File(s) Now! »
Method
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Method
One method is not more suitable than the other within scientific research, rather it depends on the problem and purpose of the research in question in order to decide which method suits better (Ghauri & Gronhag, 2010). The optional substitution to qualitative routines is the quantitative method. The main difference that differ them is that quantitative processes entail figures, statistics and quantified measures (Bryman & Bell, 2007). Furthermore quantitative methods engage in decision making of the category measures before conducting a research. The data assembled with this method are standardised implying that each unit in the study will be treated uniformly. Furthermore, qualitative methods commonly include some kind of interviews or observations. It is important to state that the two methods are not mutually exclusive and a paper can indeed include a combination of the both. A qualitative technique involves unstructured and semi-structured interviews, whereas a quantitative approach emphasises more on questionnaires that can be put on a scale (Ghauri & Gronhag, 2010).
The decision to use a qualitative method for this thesis is partly based on the quote “Qualitative research is a research strategy that usually emphasises words rather than quantification in the collection and analysis of data,” (Bryman & Bell, 2007, p. 402). With the qualitative approach the relationship between banks’ customer relationship and social media utilisation will be explored. According to Jacobsen (2002) the central advantage of the qualitative technique is the open and untied information acquiring. Crewsell (2003) further added the dimension of gaining diversity in information.
One of the most important factors when deciding the method was the advantage of flexibility. The topic of this paper is relatively novel and the possibility to change and refine the problem formulation and purpose during the course of the study was of the essence for the research. As the qualitative method is untied and not strict to information it can allow the characters to describe their understanding of the topic (Jacobsen, 2002).
As this thesis has been concentrated to one specific bank, SEB, the qualitative approach allowed focusing on this chosen company (Jacobsen, 2002). The method allows meetings, interviews and interactions with the people in the organisation and receives a fair view of the real case. The qualitative technique further presents the opportunity to locate details as a focal point (Bryman & Bell, 2007). Using this tool it allocated focus on the respondents within the study and their view. The relationship between social media and increased customer relations was investigated and how the bank and its’ employees observe the phenomenon.
However there are some disadvantages that require to be mentioned with the chosen method of qualitative technique. One of those is the disadvantage of complexity of replication of the study. To meet this difficulty the investigator needs to emphasise one particular area within a study while the other areas are put aside (Bryman & Bell, 2007).
As mentioned this thesis is committed to a qualitative method as the most suitable means for the purpose. In this way the investigation of the purpose and focus on specific details and expressions is facilitated (Bryman & Bell, 2007). Furthermore the qualitative technique offers the opportunity to collect wide information from human resources at SEB. The chosen information collection method is semi-structured interviews. This technique is further presented in section 3.4.1. Since social media is a rather new topic within business and there is little know on how it works within banking, a qualitative study can provide more elaborated details and understanding than a quantitative study. Moreover the study will be focused on one retailing bank, thus a qualitative method containing flexibility and unstructured in-depth insight is appropriate.
Induction vs. Deduction Approach
An inductive approach is merely on empirical findings, whereas logic is the key ingredient within a deductive approach (Ghauri & Gronhag, 2010). With induction, the research begins with observation, followed by findings, and ends up with building a theory. The new built up theory most often becomes a result of a qualitative type of research (Ghauri & Gronhag, 2010). On the other hand, the deductive approach draws conclusions through logical thinking by forming hypotheses from existing knowledge, which after tested in the empirical study can be either accepted or rejected. Consequently, a deduction starts with an existing theory, which is tested throughout the research, and is associated with a quantitative research process (Ghauri & Gronhag, 2010).
Even though this paper is not building up a new theory, it is more close to an inductive approach, which is therefore used to be able to reflect upon different theories after qualitative research is done. There is also no hypothesis testing involved in the study that can refer to a deductive approach.
Research Design
Anderson (2004) describes three different research types including exploratory which gains new insight through qualitative data, descriptive which contains outlines of people or situations, and finally the explanatory research type which is used for this paper since it is able to understand a problem or situation with the help of why and how questions.
An exploratory study is usually accompanied when there is restricted or no material about the research topic. The intention is then to get a deeper understanding of the problem. One method of doing it is by conducting interviews (Sekaran, 2003). An explanatory research is appropriate when the objective is to describe how and/or why a certain occurrence arises. This type of investigation tries to relate the source and the action of the study subject (Jacobsen, 2002). A descriptive study method is appropriate when the investigator wants to examine the features of the variables in the research. The goal is to define significant characteristics of the examined problem. Typically a descriptive study is used when characteristics of a study is researched. This thesis is done according to an explanatory technique. Even though the purpose of the thesis is stated with a “what” question, the respond and related research questions answers to how and why Facebook can be used in relationship marketing. A descriptive research approach will be taken to portray the phenomenon. However, the research design is more explanatory related, as a further ambition is to explain why Facebook could be implemented in banking. It has been chosen to construct a case study. The choice of the company will be provided in the next section.
Choice of Company
The focus of this thesis is on personal retail banking and the relationship between the bank and the private persons. SEB is describing itself as a relationship bank that put effort into maintaining their customers in the best possible way. In the end of 2010, SEB implemented a wide spread social media, which is Facebook. They have employed a group of professional bank employees who are offering customer service with quick answers for their customers’ questions. The group is available Monday to Friday between 8 am until 10 pm. SEB was chosen to do an investigation in, since it suited the criteria to study the connection between relationship marketing and social media implementation in a bank.
Company Background
SEB (Skandinaviska Enskilda Banken AB) was established in 1856 and is today occurring around Europe. The bank is focusing on international presence, entrepreneurship and on a concern for long-term relationships. SEB offers its private customers and companies the promise of a fruitful relationship and the bank is constantly trying to think in innovative ways, eyeing for new ideas, markets and people. SEB describes itself as making the life easier with a contribution to the society’s development. It wants to be seen as a bank that stands for good ethic with lasting development in all of its operations. SEB wants to help companies and private customers to reach their financial goals, which would lead to a positive development and economic welfare. Further contributions made for the society’s development is the creation of more work opportunities and the buying and selling of services and goods from a broad amount of suppliers (SEB, 2010).
SEB provides services for approximately 400 000 companies and institutions and to more than five millions private customers. The bank has around 17 000 employees where more than half of them are working outside of Sweden. The bank is established around the world in 20 countries such as in Denmark, Finland, Germany and Norway and has established offices in all major financial centres such as Shanghai, New York and London. SEB’s vision is to be a reliable partner for its customers with the mission of helping individuals and businesses with advice and financial resources so that they can do well (SEB, 2010).
Continuity, mutual respect, professionalism and engagement are all values that play the core of SEBs brand. The bank learns and acts along its long experience and is open-minded with the aspiration to earn its customers’ as well as employees’ trust. SEB wants to make it easier for the customers when doing business by sharing experiences and taking a full commitment for their acts in an attempt to make the bond stronger. The goal is to create value for all stakeholders, employees and customers. To be able to reach the long-term goal the bank has set up a strategy that is called “road to excellence”. SEB wants to reach more growth within the cornerstones of the bank, which is investment banking, services for companies, fund insurances, and investment management (SEB, 2010).
Data Collection
The theoretical framework was built up by using applicable academic theories for the purpose that was later combined with the empirical primary data. The literature assortment for the theoretical framework was collected from articles, books, databases and other Internet sources. The primary data was conducted by collecting new material for the given purpose of this thesis (Burns, 2000). The primary data collection method that was selected was in depth interviews.
Interviews
The information collection procedure that was chosen was semi-structured interviews. This method is a combination of controlled and untied questions (Gillham, 2005). This facilitates the interviewer to raise supplementary questions if the first responses are not satisfying (Williamson, 2002). In the collection, interviews and insights were received from different people within the organisation, which is why different interview guides were conducted. The questions were the same to the entire group of respondents while some added questions were formed specifically to one person working explicitly with the Facebook project. Before conducting the interview guide a minor pilot study was carried out in Jönköping. This pilot study was aimed at giving a view of the trends and reflections of the public’s relation to social media and banking. The study was conducted as a preparation and practice for the authors and will not have any greater importance in the actual thesis. The interview questions are provided in Appendix 1.
The interview guide and questions have been developed especially for this research by the authors of this thesis. With the help of cues the interviewer has the tool to guide the interviewees to get correspondence in the subject of concern (Gillham, 2005). The aim is to assemble information from different interviewees with questions to facilitate an answer to the purpose of the thesis. The interviews were structured but during the interviews the order of the questions could differ as well as the follow-up questions, all depending on how the respondent replied. By using this technique there was a focus to reach the goal with the interviews without limiting the respondents from expressing their own point of view.
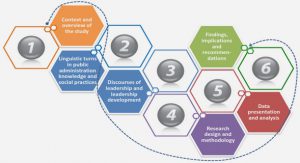
1 Introduction
1.1 Background
1.2 Problem Area
1.3 Purpose
2 Theoretical Framework
2.1 Service Company
2.2 Bank Marketing
2.3 Relationship Marketing
2.4 Service Related Technology .
3 Method
3.1 Qualitative vs. Quantitative Method
3.2 Induction vs. Deduction Approach
3.3 Research Design
3.4 Data Collection
3.5 Limitations
3.6 Trustworthiness of Data
3.7 Data Analysis
4. Empirical Findings
4.1 Bank Marketing
4.2 Relationship Marketing
4.3 Service Related Technology
5 Analysis
5.1 Bank Marketing
5.2 Relationship Marketing
5.3 Service Related Technology
6 Conclusion
Figure 1
7. Recommendations and future research
7.1 Recommendations
7.2 Future Research
References
GET THE COMPLETE PROJECT
Facebook in the Banking Industry A Case Study in SEB Sweden